+86-18667862027
Web Menu
Product Search
Exit Menu
Does the glass electric kettle have a silent heating function?
General Heating Characteristics of a glass electric kettle
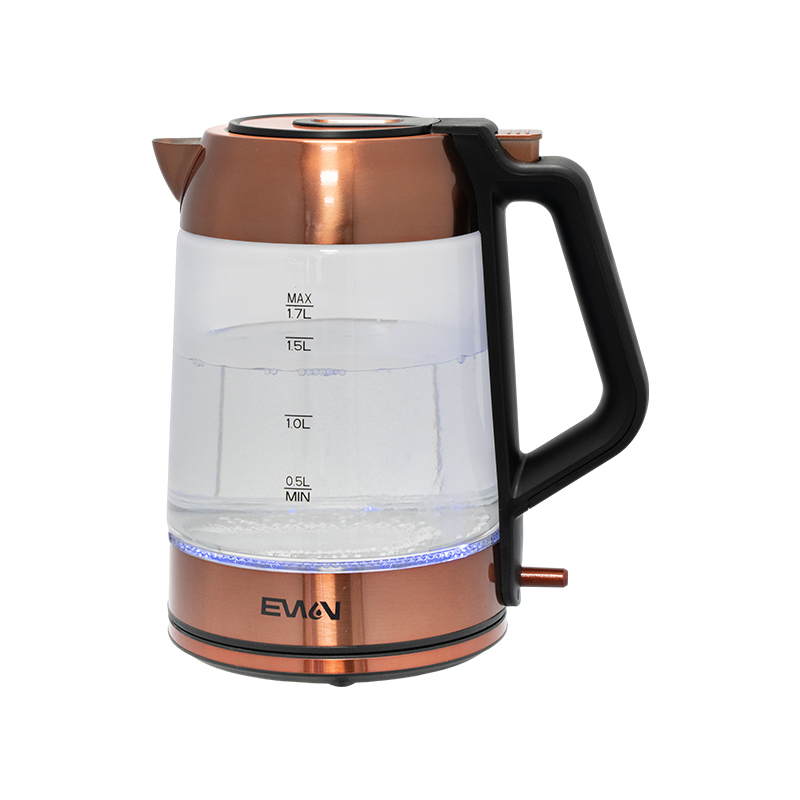
When discussing whether a glass electric kettle supports a silent heating function, it is essential to first understand the general heating behavior of such appliances. A glass electric kettle typically uses a concealed heating element at the base, allowing water to warm through conduction as the heating plate increases its temperature. This process naturally produces some sound because water molecules become active as temperature rises, creating small vibrations, bubbling, and occasional metallic resonance from the inner plate. The structural nature of glass contributes to acoustic transparency, meaning it does not significantly soften or dampen heating noise in the way thicker stainless steel shells sometimes do. As a result, silence is influenced not only by the heating mechanism but also by the physical properties of the glass body, its thickness, shape, and how securely components are assembled. Although many modern devices aim to reduce distracting sound, it is important to understand that a glass electric kettle may still generate some noise due to boiling physics, regardless of design efforts.
Design Factors That Influence Noise Levels
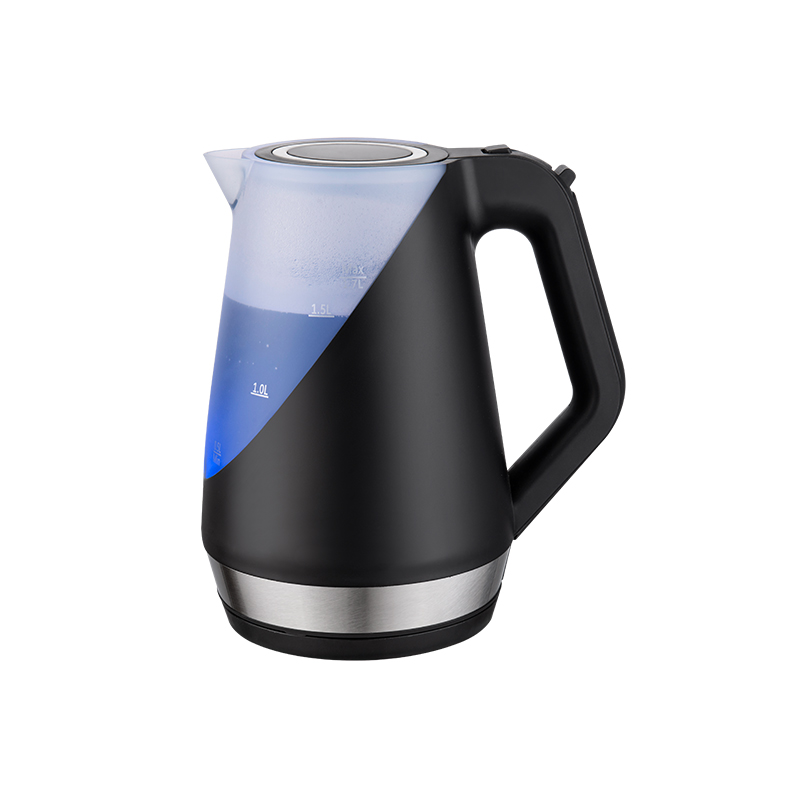
Noise level in a glass electric kettle is influenced by several design details, such as the base plate’s thickness, the fit of the lid, and the stability of the kettle on its heating dock. A well-structured kettle base that maintains firm contact with the heating plate may generate a quieter operation compared with one that sits loosely or transfers vibration into the glass body. Lid structure also matters because pressure buildup during heating creates air movement that can make subtle sounds if the lid seal is not uniform. Additionally, the capacity of the kettle influences how much noise boiling water generates; larger volumes of water will produce a deeper bubbling pattern while smaller amounts may boil quickly and generate short bursts of sound. The handle and frame connecting the glass chamber to the base can also transfer vibration if not properly stabilized. In this sense, the noise level is the sum of heating physics plus the construction quality of the kettle.
Silent Heating Technology Explained
Silent heating functions used in some modern devices are designed to minimize operational sound, and several approaches can be implemented in a glass electric kettle. A common strategy is the use of a low-frequency heating cycle in the early stages of warming, which helps reduce sudden acoustic changes. This method preheats water gradually to avoid abrupt bubbling or vibration. Another principle involves enhancing the insulation beneath the heating plate so less vibration transfers into the counter surface. Some kettles use reinforced glass, which provides better structural rigidity and absorbs a portion of vibration, thereby contributing to a softer sound profile. However, the silent heating effect is limited by the fact that water boiling naturally produces sound as energy is released through bubbles. For this reason, silent heating technology focuses more on softening mechanical and structural noise rather than eliminating the sound of boiling itself.
Material Influence on Acoustic Performance
The material composition of a glass electric kettle plays an important role in sound behavior. Glass, being a rigid material, does not inherently absorb vibration. When heated, the contact between hot water and the glass body sometimes creates slight crackling or tapping sounds as the temperature changes. Compared with plastic kettles, which may absorb a small portion of vibration, a glass model will usually transmit more natural boiling sound. However, thicker borosilicate glass can offer better temperature resistance and more stable acoustic transmission, reducing unwanted vibration noises. Meanwhile, the heating plate material, usually stainless steel, contributes to the sound profile by controlling how even and stable the heat distribution is. Smooth and uniform plates provide more stable heating, while uneven or thinner plates may produce slight clicking noises as they expand and contract. As a result, material considerations affect whether a glass electric kettle can support a heating process that appears quieter.
Consumer Expectations of Silent Operation
Consumer expectations surrounding silent operation vary widely. Many users assume that a glass electric kettle with silent heating function should operate almost inaudibly, but this expectation does not fully align with the natural behavior of boiling water. Manufacturers often clarify that silent or low-noise designs reduce structural noise rather than the boiling sound itself. A glass electric kettle may therefore seem quieter during the pre-boiling stages while still producing bubbling and steam sounds at high temperatures. The goal is usually to minimize mechanical noise such as rattling, metallic clicking, or lid vibration. Some consumers appreciate a moderate level of sound because it signals boiling progress without requiring direct observation. Others prefer the kettle to generate as little noise as possible due to personal comfort or to avoid disturbing quiet environments. These expectations influence design trends and how manufacturers define silent heating capabilities.
Comparison of Noise Levels in Different Heating Modes
Because heating modes vary, a glass electric kettle may behave differently depending on temperature control design. Some kettles use straightforward boiling mode, turning on the heating element at full power until water reaches boiling point. Others employ stepped heating modes, where lower power levels operate during early warming. The stepped approach tends to create a smoother sound profile. Advanced models with multiple temperature settings such as 40°C, 60°C, 80°C, and 100°C may produce different intensity levels of bubbling, because water near boiling point releases larger air pockets. Manufacturers sometimes include “quiet boil” modes, which adjust heating intensity to reduce turbulence. In contrast, rapid-boil functions prioritize speed and may increase bubbling sound. The type of heating system therefore determines whether a glass electric kettle can support functions that appear quieter to the user.
| Heating Mode Type | Typical Noise Level | Noise Source | User Application |
| Standard Boil | Moderate bubbling noise | Natural boiling turbulence | General daily use |
| Stepped Heating | Softer heating sound | Lower power cycling | Controlled warming |
| Quiet Boil Mode | Reduced mechanical noise | Stabilized heating plate | Low-noise environments |
| Rapid Boil | Higher bubbling sound | High power input | Fast boiling |
Role of Base Design and Heating Plate Structure
The structure of the base and the configuration of the heating plate directly influence how much noise is created during heating. A glass electric kettle depends on the base to deliver uniform energy across the heating surface. If the plate is engineered for even heat distribution, the formation of large vapor pockets is minimized, which can soften the intensity of boiling sound. In contrast, uneven heating zones can create sudden bursts of bubbles that create sharper noise. The base also acts as a stabilizing platform. Bases with anti-slip construction and weight balancing features reduce mechanical vibration. Some models include acoustic pads beneath the base housing to absorb sound resonance traveling from the heating element. Even though the primary noise source is boiling water, a stable heating base helps maintain a consistent sound profile during use.
Impact of Water Quality on Heating Sound
The mineral composition of water can influence the sound produced in a glass electric kettle. Water containing high levels of calcium or magnesium tends to cause more rapid nucleation inside the kettle, meaning bubbles form more quickly and sometimes with greater intensity. This can increase boiling sound. On the other hand, filtered or low-mineral water boils more evenly, which may lead to a softer sound profile. Scale buildup on the heating plate can also affect noise levels by creating uneven surfaces where bubbles form unpredictably. This highlights the importance of regular descaling routines. A clean heating surface helps maintain stable performance and predictable acoustic behavior. Because water quality varies across regions, the level of noise associated with heating cannot be attributed solely to the design of a glass electric kettle.
Advantages of Silent Heating Designs
Silent heating designs offer several practical advantages related to comfort and usability. A glass electric kettle with noise reduction engineering is suitable for shared living spaces, office environments, or settings where users want to maintain a quiet atmosphere. Reduced mechanical sound may contribute to a more pleasant experience during early mornings or late evenings. Additionally, silent heating features reflect careful structural design, which indirectly contributes to better internal stability and durability. While the natural sound of boiling cannot be eliminated, lowering structural noise can improve user perception of product refinement. This encourages manufacturers to explore more thoughtful construction techniques such as reinforced glass, insulated bases, and improved lid-fitting mechanisms.
Limitations of Achieving Complete Silence
Although a glass electric kettle can incorporate several design methods to reduce noise, complete silence is not realistically attainable due to the physical nature of boiling water. Bubble formation, steam release, and internal pressure changes inherently generate sound. The transparent walls of the glass chamber allow users to see these reactions, but they also transmit acoustic energy outward. Therefore, silent heating capability should be interpreted as noise reduction rather than full noise elimination. Manufacturers often provide clear guidelines so users understand that lower noise refers to mechanical components rather than boiling sound. As long as water undergoes phase change, bubbling noise will be part of the process.
| Noise Source Category | Reduction Potential | Explanation |
| Mechanical Vibration | High | Design adjustments can stabilize structural components |
| Heating Plate Expansion | Moderate | Smoother plates reduce clicking sounds |
| Boiling Water Turbulence | Low | Turbulence is natural and cannot be fully removed |
Practical Considerations for Users Selecting a Low-Noise Model
When selecting a glass electric kettle with the intention of reducing noise level, users should evaluate design features such as base stability, heating plate structure, lid seal integrity, and glass thickness. Models that incorporate gradual heating control or multiple temperature settings typically offer smoother acoustic behavior. Consumers may also consider the capacity of the kettle, because larger chambers produce different sound patterns. Reading technical specifications, checking product descriptions related to quiet operation, and considering maintenance steps like descaling can help users find a model aligned with their expectations. Sound perception varies among individuals, so selecting the right kettle involves matching personal preference with practical design features.
address
No.935 Qiye Road, Zhouxiang Town, Cixi City, Zhejiang Province, China
Sale’s Email
leila@nbewin.com
sales8@nbewin.com
sales9@nbewin.com
Copyrighte Ningbo Ewin Electrical Appliances Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved.